Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB): Comprehensive Guide with Best Practices
Zero-based budgeting (ZBB) remains a valuable approach for organizations seeking sustainable cost management with effective organizational design.
Explore our comprehensive guide on position management in HR. Learn 10 best practices, challenges, top trends for effective organizational efficiency.
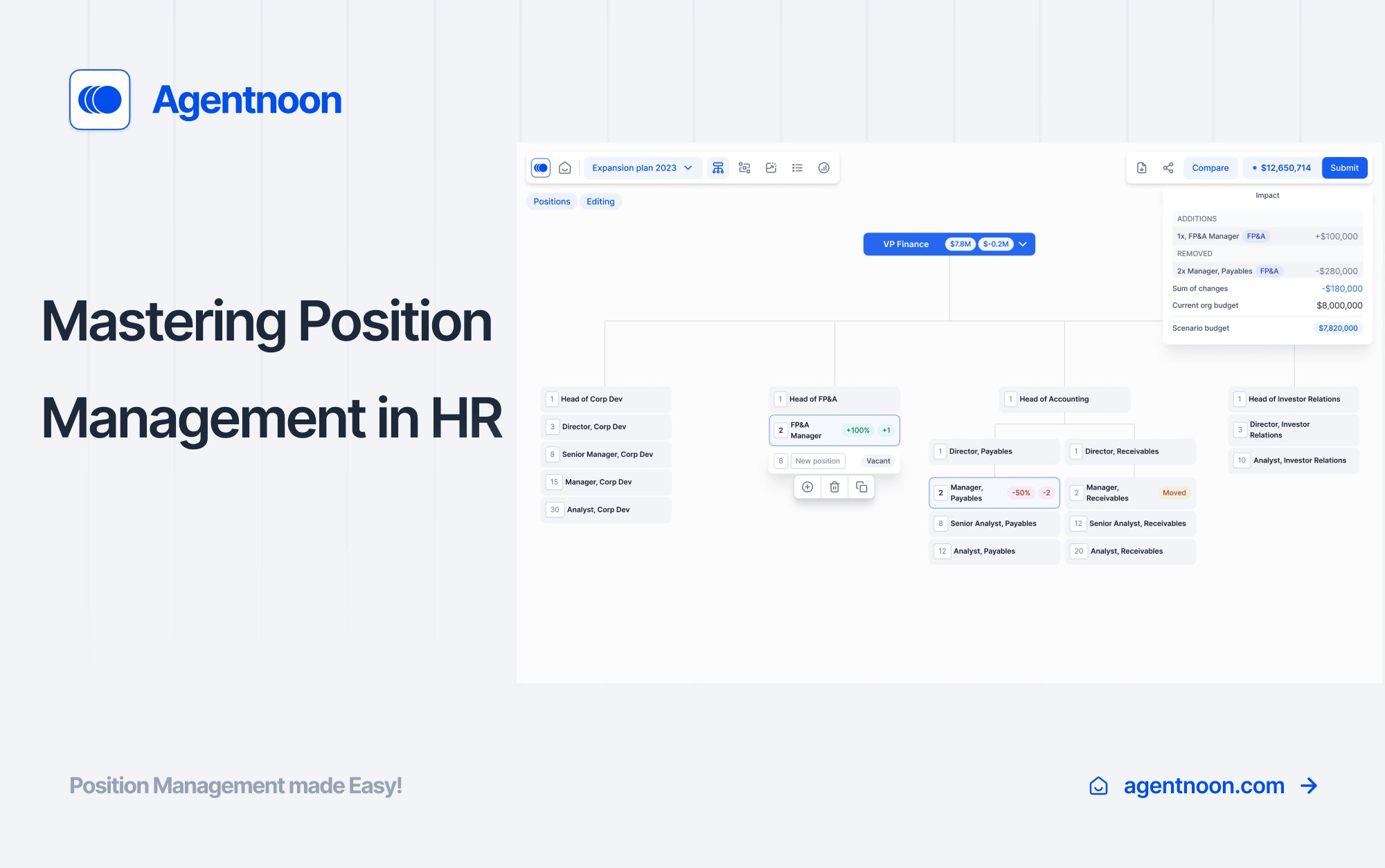
In the realm of Human Resources, position management or position control stands as a pivotal strategy, crucial for effective workforce planning and organizational efficiency. This approach, focusing on managing positions rather than individual employees, offers HR leaders a powerful tool for aligning their workforce with the strategic goals of their organization.
At its core, position management also called position control is the process and technology used to define and maintain positions within an organization, independent of the employees filling those roles. This approach involves specifying the number of positions, setting hiring rules, and tracking each position's unique attributes, such as department, salary range, and required qualifications.
Unlike job management, which is more employee-centric and less structured, position management demands a more detailed approach. It requires a comprehensive understanding of each role within the organization and how these roles interact with one another. This level of detail and coordination, while more complex, yields greater efficiencies and accuracy in workforce planning, budgeting, and internal mobility opportunities. This approach ensures that each role is clearly defined in terms of responsibilities, required qualifications, and salary range. The result? A systematic alignment of human resources that supports efficient budgeting and strategic planning. Through position management, companies can navigate workforce complexities with ease, ensuring that every role contributes optimally towards organizational objectives.
Strategic Alignment: Effective position management aligns seamlessly with an organization's business strategy. It plays a vital role in workforce planning, succession planning, and budget analysis, ensuring that the human capital management strategy mirrors the budgeted positions and organizational goals.
Case Studies: Consider a healthcare organization implementing position management to handle complex workforce structures, such as employees working across multiple roles or programs. This approach allows for accurate payroll compliance, efficient budget forecasting, and a clear understanding of workforce dynamics.
Streamlining HR Processes: Position management enhances the speed and accuracy of workforce planning, succession planning, and organizational recruiting. It leads to improved human capital reporting and payroll accuracy, making the HR processes more efficient and data-driven.
Enhancing Workforce Planning and Analytics: With a clear view of the entire workforce, position management aids in budget-to-actual analysis and provides valuable insights for strategic decision-making, helping HR leaders to manage their workforce proactively.
Implementing position management can be challenging, especially when integrating new systems. Aligning various departmental objectives with the overall organizational strategy requires meticulous planning and coordination. One of the significant hurdles is ensuring all staff are adequately trained for the transition, which can be a complex process given the diverse nature of roles within any organization.
Implementing position management / position control can be challenging, requiring consistent processes, approval protocols, and effective coordination across finance and HR departments. Change management is a critical component, often requiring a significant shift in organizational mindset.
Maintenance poses another set of challenges. Keeping position descriptions updated and adapting them to organizational changes is crucial for retaining the system’s relevance. As a company evolves, so do its goals and needs, necessitating regular adjustments to position structures. This continuous updating process ensures that the position management system remains aligned with the current and future goals of the organization. Successful position management requires ongoing monitoring and regular maintenance to ensure that the positions accurately reflect the current organizational structure and strategy.
Position management, essential in modern HR, requires a well-thought-out strategy and ongoing attention. Here are some of the best practices:
Effective position management starts with a thorough analysis of the workforce. It's about understanding the total workload and dividing responsibilities efficiently. This analysis is the cornerstone, ensuring that each role is essential and aligns with the organization's strategic goals. It involves assessing the current state of the workforce, identifying gaps or redundancies, and anticipating future needs based on organizational growth and market trends. This step is critical for creating a workforce blueprint that is not just responsive to current needs but also adaptable to future changes.
A pivotal aspect of position management is aligning workforce needs with financial capabilities. It's not just about filling positions but doing so in a financially sustainable way. This practice involves detailed budget planning and analysis, considering factors like salaries, benefits, training costs, and potential ROI of each role. By aligning human capital needs with budget constraints, organizations can avoid overstaffing or underutilization of resources. This balance is crucial for maintaining financial health and ensuring that human resource investments directly contribute to the organization’s bottom line.
Assigning unique identifiers to each position within an organization is a best practice that aids in effective management. Especially in larger organizations with diverse roles, this system helps in accurately tracking and managing each position. Unique identifiers simplify the organization of a complex workforce, making it easier to manage payroll, performance evaluations, and career development pathways. This system also aids in eliminating confusion and ensures that every role is clearly defined and accounted for in the organizational hierarchy.
Defining each position with specific attributes is crucial for clarity and alignment with organizational needs. Attributes like department affiliation, work periods, employee classification, and compensation details bring a level of detail that is vital for effective position management. This granularity ensures that each role is tailored to meet the unique needs of the department and the organization as a whole. It also facilitates better alignment with the overall organizational structure, aiding in strategic workforce planning and resource allocation.
Innovative position management heavily relies on data-driven insights. Creating new positions is not about guesswork but using historical performance data and future projections. Analyzing past trends helps in understanding which roles have been most effective and where gaps exist. Future projections, on the other hand, guide the creation of roles that align with where the organization is heading. This approach ensures that every new role serves a strategic purpose and contributes to the overall objectives of the organization.
Uniformity in managing position-related changes is critical. Standardizing processes for updating and managing positions ensures consistency and alignment with the organization's broader goals. This standardization includes establishing clear guidelines for creating, modifying, or removing positions, and ensures that every change is made systematically and with a strategic rationale.
Anticipating employee turnover is an essential aspect of position management. By understanding turnover trends, HR can proactively plan for vacancies, ensuring that critical roles are always filled, and productivity is maintained. This foresight allows for smoother transitions and minimal disruption to operations.
Developing engagement strategies that cater to the specific needs of various positions is vital. Employee engagement drivers can differ significantly between roles and organizational levels. Tailoring these strategies ensures that employees are not only satisfied but also motivated and aligned with their roles, leading to higher performance and reduced turnover.
Establishing well-thought-out promotion cycles is key to both employee satisfaction and organizational growth. These cycles should mirror the organization's operational needs and the career aspirations of its employees. Regular, strategically timed promotions help maintain employee motivation and contribute to the organization's dynamic development.
Maintaining up-to-date position data is crucial, especially when dealing with employee departures. Regular updates ensure that the organization's workforce structure accurately reflects current needs and strategies. This practice is essential for keeping the organization agile and responsive to both internal changes and external market dynamics.
Expert Tips: Leverage insights from trusted advisors who are familiar with the tools and common deployment challenges. Focus on areas like headcount budgeting and identifying reporting gaps that can be addressed through effective position management.
Tool Overview: Select tools that offer comprehensive features for creating, managing, and integrating positions with other HR processes. Consider your organization's size, existing technology infrastructure, and specific needs when choosing software.
Choosing Software: Evaluate whether a unified platform or a 'best of breed' approach is more suitable for your organization. Look for solutions that can leverage your existing technology investments and enhance your position management efforts. Tools like Agentnoon can integrate with 100+ HRIS, ATS tools, providing a versatile and comprehensive solution for your position management needs
Emerging Technologies: The future of position management is likely to be shaped by advancements in AI and machine learning, automating many of the processes and enhancing the overall efficiency and effectiveness of position management strategies.
Future Predictions: Expect a closer integration of position management with strategic planning and a greater emphasis on agility and adaptability in workforce planning.
Position management is an essential component of modern HR, offering strategic alignment, enhanced process efficiency, and insightful workforce analytics. Embracing this approach is crucial for achieving organizational success in today's dynamic business environment. For organizations looking to implement or enhance their position management strategy, consulting with Professional Services experts can provide tailored guidance and support.
Get in touch with us to learn more about how Agentnoon can help you with your position management needs!
Zero-based budgeting (ZBB) remains a valuable approach for organizations seeking sustainable cost management with effective organizational design.
Discover how to maximize business growth with our comprehensive guide on workforce analytics. Learn key strategies for data-driven decision-making.
Explore the top 10 organizational design metrics essential for business success, including employee engagement, turnover rate to optimize your...
